前言:
这篇应该也是拖了两个多月了,很烦,现在来补坑来了。Sorry..
正文:
这是一个在跑安服的朋友给我的一份病毒样本,让我帮忙分析分析,找到攻击目标和残留后门以便于清理后门。花时间分析了一下发现是一个DDOS的样本,值得我写一写分析过程。
他发给我的是一个文件夹,打开后有两个程序和一个文件夹。
不过这个叫beijing名的程序当时给了我一个很奇怪的感觉。。事实证明我的感觉是正确的,这个程序是某网杯一道简单的逆向题…为什么给我的样本里面还有题…算了,继续分析下一个soft程序。先查看一下所有的字符串找一找有用的信息:
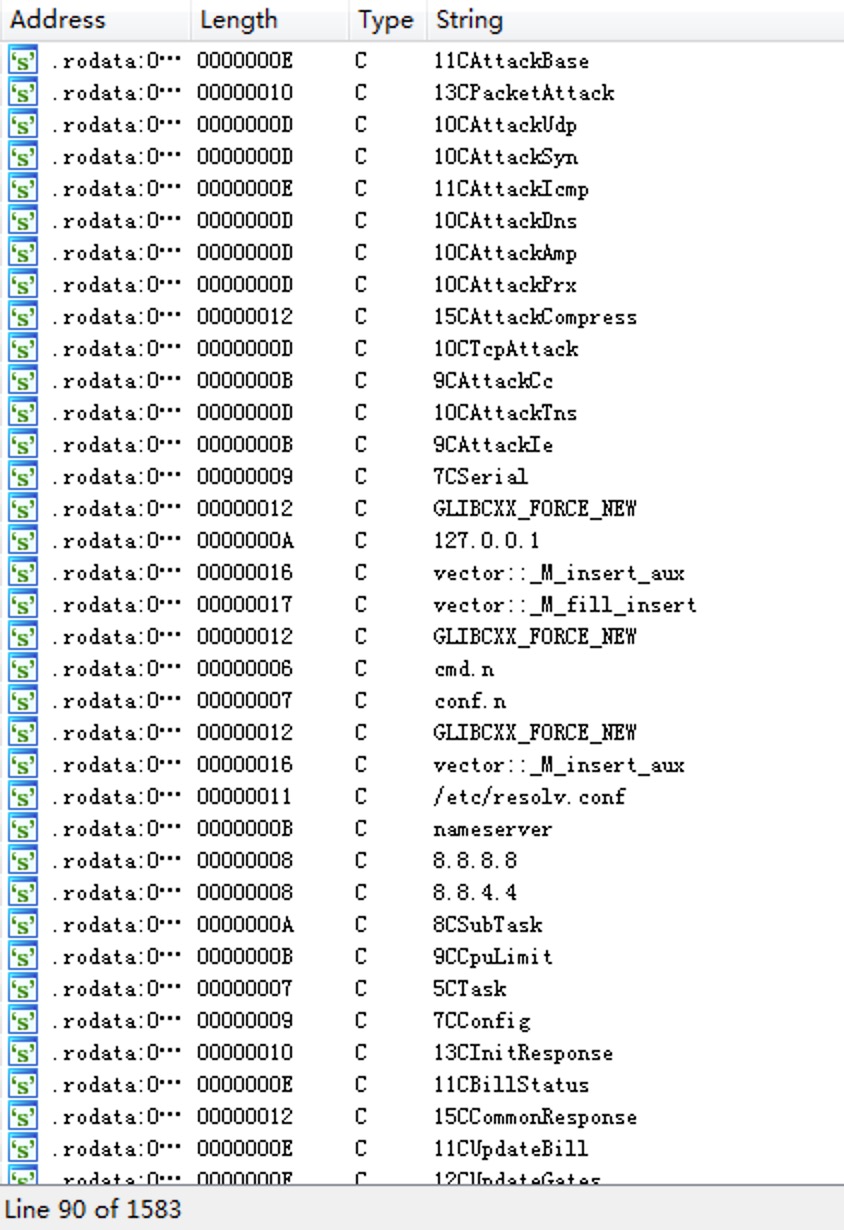
有些attack字样的字符串,以及http协议、一大堆IP地址等:
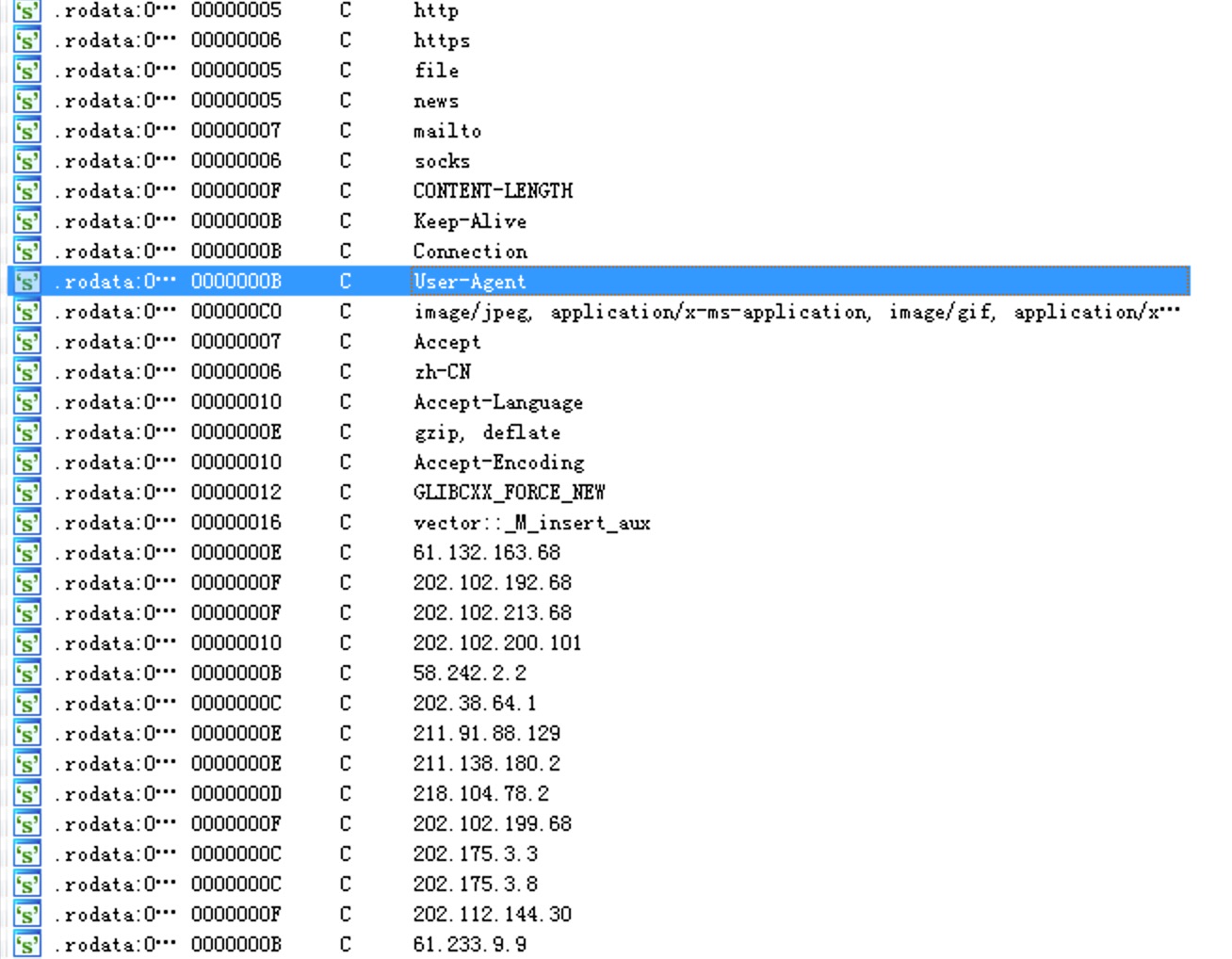
开始分析,看主程序:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| v3 = alloca(16);
CSysTool::CloseAllFileDescs();
CSysTool::Ower6msf(); // 第一组数据解密
std::string::string((std::string *)&v11);
CUtility::GetModuleFullPath((CUtility *)&v11, v8);
v4 = (CFileOp *)std::string::c_str((std::string *)&v11);
if ( CFileOp::GetTgtFileSize(v4, v5) != g_iFileSize )
MEMORY[0] = 0;
CUtility::GetParentPath((CUtility *)&v10);
v6 = std::string::c_str((std::string *)&v10);
if ( strstr(v6, "gdb") != 0 ) // 反调试
MEMORY[0] = 0;
HGrd9((int)&v12);
std::string::operator=(&g_strSN, &v12); // g_strSN = DbSecuritySpt
std::string::~string((std::string *)&v12);
Mndyuf((int)&v13);
std::string::operator=(&g_strBDSN, &v13); // g_strBDSN = selinux
std::string::~string((std::string *)&v13);
BGtd98();
std::string::operator=(&g_strBDG, &v14); // g_strBDG = getty
std::string::~string((std::string *)&v14);
Osdku6();
std::string::operator=(&g_strML, &v15); // g_strML = /tmp/moni.lod
std::string::~string((std::string *)&v15);
wer54();
std::string::operator=(&g_strGL, &v16); // g_strGL = /tmp/gates.lod
std::string::~string((std::string *)&v16);
CSysTool::CheckGatesType(); // check GatesType
CSysTool::Ikdfu94(); // 第二组数据解密
if ( (unsigned __int8)CSysTool::IsUpdateTemporary() )
{
CSysTool::DoUpdate((CSysTool *)argc, (int)argv, v9);
}
else if ( g_iGatesType == 1 )
{
MainBeikong();
}
else if ( g_iGatesType > 1 )
{
if ( g_iGatesType == 2 )
{
MainBackdoor();
}
else if ( g_iGatesType == 3 )
{
MainSystool(argc, (char **)argv);
}
}
else if ( !g_iGatesType )
{
MainMonitor();
}
|
先看第一组解密函数:

以上是第一组数据解密后的变量。再来看第二组解密后的:
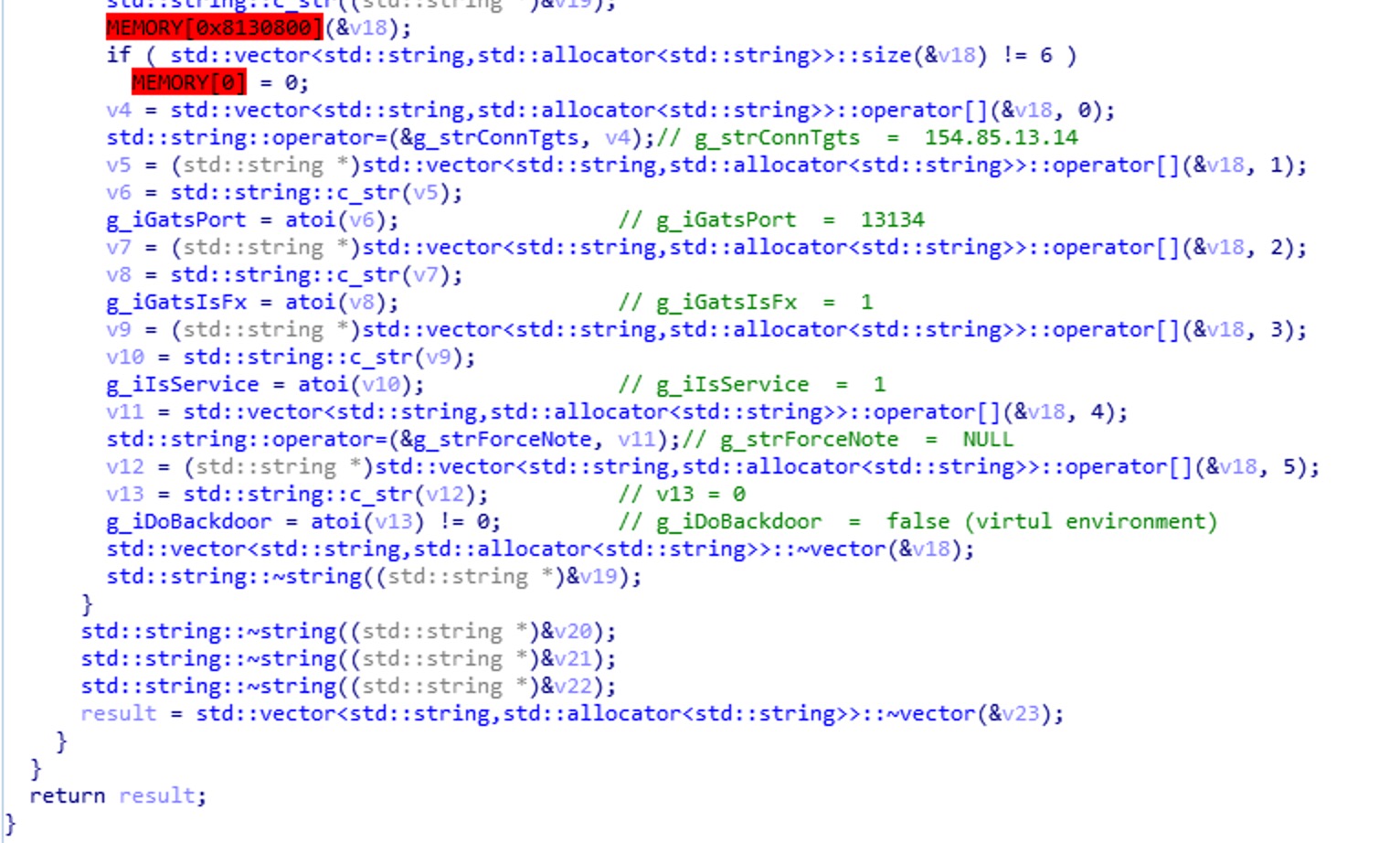
再来观察查询g_iGatesType的值的函数:
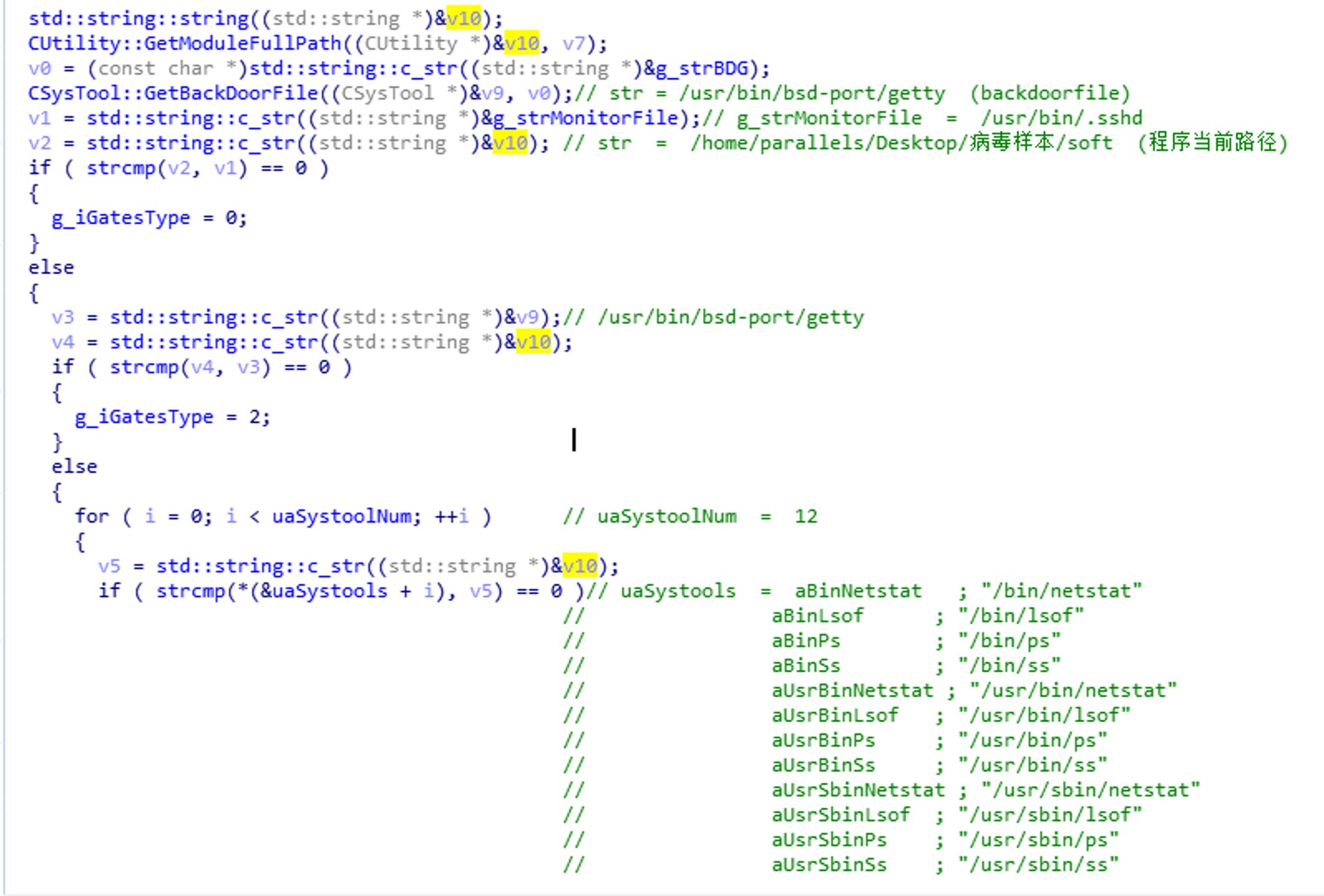
以上函数用来对比当前程序所在的目录,如果与MonitorFile路径相同,GatesType则为0,与BackDoorFile相同,GatesType则为2,如果与Systools中的任何一个路径相同,GatesType则为3,否则为1。
集合起来就是:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| g_iGatesType = 0 /usr/bin/.sshd
g_iGatesType = 1 其他路径
g_iGatesType = 2 /usr/bin/bsd-port/getty
g_iGatesType = 3 aBinNetstat ; "/bin/netstat"
aBinLsof ; "/bin/lsof"
aBinPs ; "/bin/ps"
aBinSs ; "/bin/ss"
aUsrBinNetstat ; "/usr/bin/netstat"
aUsrBinLsof ; "/usr/bin/lsof"
aUsrBinPs ; "/usr/bin/ps"
aUsrBinSs ; "/usr/bin/ss"
aUsrSbinNetstat ; "/usr/sbin/netstat"
aUsrSbinLsof ; "/usr/sbin/lsof"
aUsrSbinPs ; "/usr/sbin/ps"
aUsrSbinSs ; "/usr/sbin/ss"
|
而后会根据GatesType的值来执行不同的功能:
GatesType == 0:
执行MainMonitor函数:
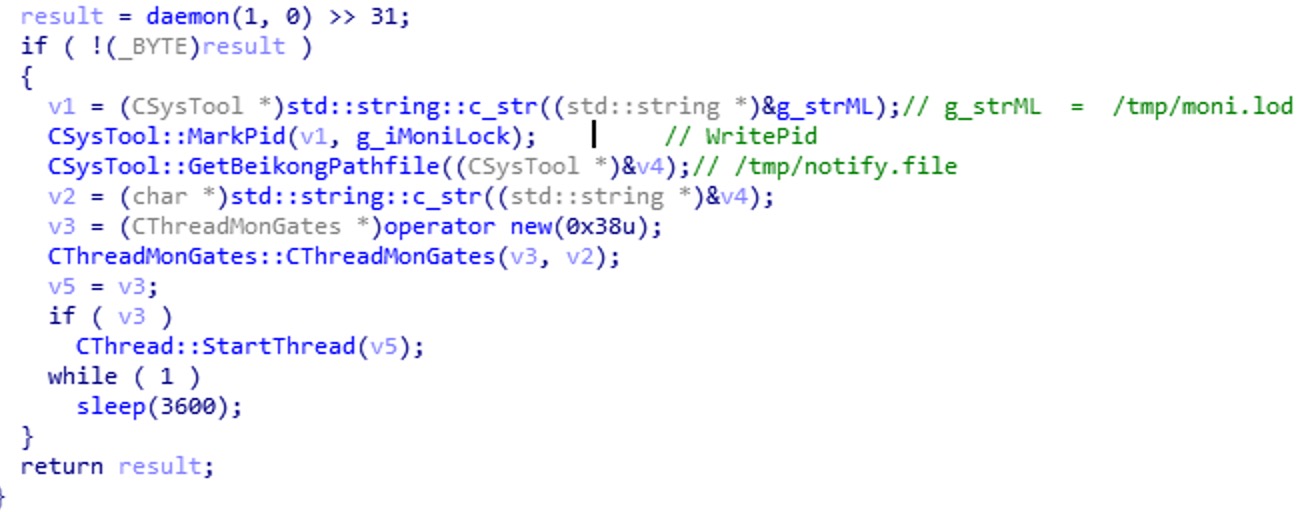
创建子进程并向/tmp/moni.lod文件写入进程号,读取并删除/tmp/notify.file文件,线程循环挂起一分钟。
GatesType == 1:
执行MainBeikong函数:

结束并删除/tmp/moni.lod进程。创建自启动项/etc/init.d/DbSecuritySpt,并写入#!/bin/bash\n(filepath)\nfilepath为当前程序路径。创建自启动项/etc/rc(1-5).d/S97DbSecuritySpt,执行ln -s /etc/init.d/DbSecuritySpt (filepath)创建软链接。
判断当前g_iDoBackdoor的值以及当前进程是否为root用户创建,如果都为true,则结束/usr/bin/bsd-port/getty.lock进程和/usr/bin/bsd-port/udevd.lock进程,并删除第二个文件。并且命令执行拷贝进程文件于/usr/bin/bsd-port/getty。
如果是root执行的程序,则命令执行拷贝进程文件在/usr/bin/.sshd。
如果不是root执行的,则删除/tmp/notify.file。
最终执行MainProcess函数,删除进程路径下的update_temporary。在/etc/resolv.conf下添加DNS(8.8.8.8和8.8.4.4)。初始化conf.n和cmd.n文件,初始化计算机基本信息(cpu、os、net、内存和磁盘信息)。初始化330个DNS地址。读取/usr/lib/libamplify.so文件配置amp资源数据。
后面就是服务端根据受害者计算机返回的信息,初始化数据执行对应的DDOS攻击:

GatesType == 2:
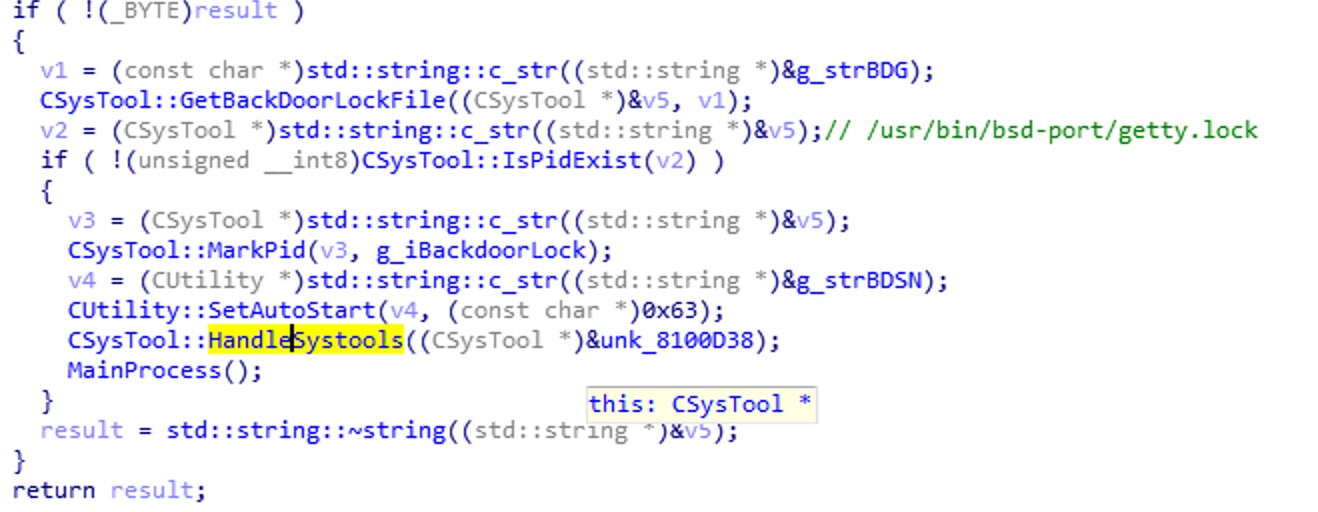
判断是否存在/usr/bin/bsd-port/getty.lock后门文件,存在则写入进程号并创建etc/init.d/selinux和/etc/rc(1-5).d/S99selinux启动项文件,之后和上面创建启动项相同,不过项目换了一个,就不多说了。然后判断如果存在Systools中的文件,则复制到/usr/bin/dpkgd/md文件下生成netstat,lsof等文件,并设置0755权限,最后又执行了同上面一样的MainProcess函数。
GatesType == 3:
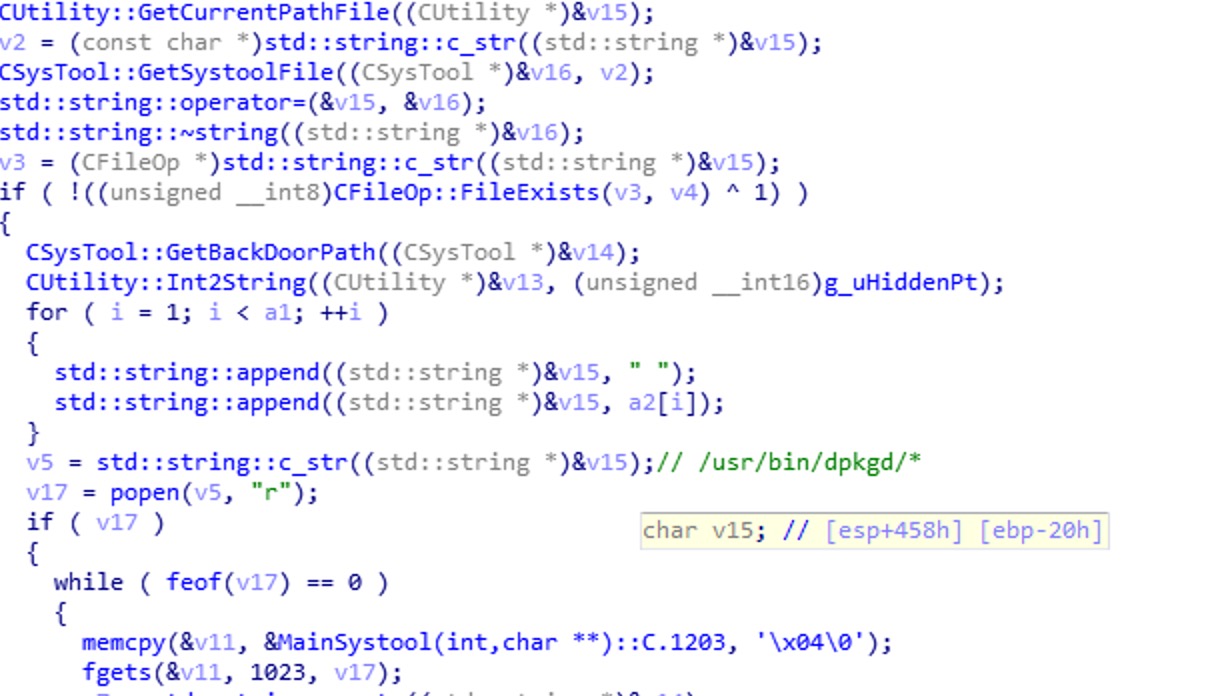
执行MainSystool函数。此函数主要调用上面所说的复制过去的netstat、lsof、ps等程序,而后过滤掉进程目录,服务端输出。
总结:
攻击者远程服务器已经找到,该木马功能为安装不同的启动项,并且安插后门,过滤木马端口信息等,生成不同路径下的副程序来持续攻击,攻击服务器根据受害机返回信息实施不同的DDOS攻击。所以样本文件中的那一组文件夹是什么东西也就很明了了。











